Psoriasis is a disease in which the skin appears red, flaky and scaly lesions covered with silvery white scales.
Usually these rashes appear on the elbows, knees, skin, scalp and lower back but can occur in any of the other places. Most people have rashes small. In some cases they can itch or hurt.
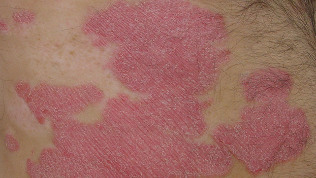
Russia psoriasis is sick about 1% of the population, often psoriasis is the most common indigenous inhabitants of the North. Men and women suffer equally often. The first psoriasis symptoms often appear before the age of 30 years, but the later the onset of psoriasis is not uncommon. The severity of psoriasis each person is very different. Someone psoriasis is just a bit annoying, when other people psoriasis prevent to live a normal life.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease, which usually has periods of remission without symptoms or mild symptoms, followed by periods of exacerbation when symptoms become more pronounced.
Psoriasis occurs when the acceleration of the process of reproduction of body cells of the skin. Skin cells are normally made and replaced every 3-4 months, but in psoriasis this process is shortened to 3-7 days. The result is the accumulation of skin cells that leads to characteristic changes in the body.
Causes of psoriasis are not fully understood, it is believed that the increased reproduction of skin cells is associated with impaired immune system. The immune system is the natural defense of the body against infections and diseases, but in people with psoriasis it mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
Psoriasis can be hereditary, and therefore, it is considered that this disease is genetic factor. However, it is still unclear what role genetics cause psoriasis.
Many people psoriasis symptoms appear or worsen after a specific event, called a trigger. Possible triggers of psoriasis include skin injuries, infectious diseases, throat and intake of certain medications. This disease is not contagious and cannot be transferred from one person to another.
If you suspect psoriasis, you should consult a doctor. Often a doctor can make a diagnosis according to the appearance of the skin. Usually diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis a patient's guide dermatologist — specialist in skin diseases.
Although a cure for psoriasis is not possible, there are several treatment methods that can alleviate its symptoms and improve the appearance of the skin. In most cases, is primarily allocated to the local treatment, for example, vitamin D analogues or corticosteroids local action. In the most severe cases, when there is no help other treatment methods, can be used for systemic treatment. Systemic treatment is the ingestion or injection of drugs, which have therapeutic effect on the whole body.
For some people psoriasis is just a minor problem, but sometimes it can greatly affect your life. For example, some people with psoriasis have low self-esteem, because of how the disease affects their appearance. Often when psoriasis appears soreness, pain and swelling in the joints and connective tissue. This is called psoriatic arthritis.
The symptoms of psoriasis
In most cases, psoriasis runs in cycles: every few weeks or months disease exacerbated, and then the symptoms become less visible or disappear, and there comes withdrawal.
There are several types of psoriasis. Many people suffer from only one form of psoriasis, although it is possible the disease of two different types at the same time. One type may change to another type or escalate. If you suspect psoriasis, you should consult a doctor.
The most common psoriasis
The usual psoriasis. This is the most common form of psoriasis, which accounts for about 90% of all cases. Symptoms of dry red skin lesions, called plaques covered with silvery white scales. They usually appear on the elbows, knees, skin, scalp and lower back but can occur in any of the other places. Plaques can itch and (or) hurt. In severe cases, the skin of the joints may crack and bleed.
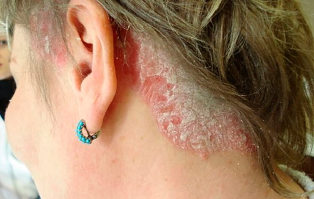
For Psoriasis of the scalp (seborrheic psoriasis) can occur in the scalp or adjacent skin, as well as the back and chest. Causing a reddish rash, covered with thick silvery white scales. Some people have this type of psoriasis causes severe itching, while others do not cause harm. In the most severe cases can lead to hair loss, often temporary.
The nail psoriasis. Approximately half of the patients with psoriasis the disease affects the nails. Psoriasis on the nails may develop small holes or bumps, they may lose their color and shape. Often, the nails may eventually become loose and move out of the nail bed, which contains. In severe cases, the nail can crumble.
Psoriasis in the form of drops occur in small (less than 1 cm) plaques in the form of drops chest, hands, feet and under the hair. High likelihood that the guttate psoriasis completely go away in a few weeks, but for some people it becomes a usual psoriasis. This type of psoriasis sometimes occurs after a streptococcal infection of the throat, and they are more common in children and adolescents.
Folds psoriasis - affects the skin folds such as the armpits, groin, between the buttocks or Breasts. Can looks more smooth eczema some or all of these areas. Symptoms are aggravated by friction and sweating, so you can deliver the particular disadvantages of the hot weather.
Pustular psoriasis
Rarer type of psoriasis, where the skin appeared blisters (blisters and purulent content). A variety of pustular psoriasis is striking different parts of the body.
Pulstole generalized psoriasis (psoriasis background Tsumbush). Blisters presence of a large surface of the skin and develop very quickly. The pus consists of white blood cells and its appearance is not always directly related to the infection. Pustules can cyclically re-appear every few days or weeks. At the beginning of these cycles of psoriasis in the background Tsumbush can cause fever, chills, weight loss and chronic fatigue.
The palms and soles of the psoriasis. Pustules appear on the palms and soles of the feet. Pustules gradually rounded brown patches, scales, which are then separated from the skin. Blisters can appear again every few days or weeks.
Pustular acrodermatitis (acrobustulosis). Pustules appear on the fingers hands and feet. Then the blisters burst, when they leave bright red areas that may bleed or be covered with scales. Can lead to painful deformities in the nails.
Erythrodermic psoriasis (psoriasis erythroderma)
Erythrodermic psoriasis is rare psoriasis, which affects almost the entire surface of the skin. It causes severe itching or burning sensation. Because erythrodermic psoriasis on the body to lose proteins and fluid. This can cause other complications, such as infection, dehydration, heart failure, hypothermia and exhaustion.
Causes of psoriasis
Psoriasis occurs when skin cells divide and are updated more quickly than usual. Causes of psoriasis are not fully understood. The body produces new cells in the deepest layer of the skin. These cells gradually move. Coming to the surface, they die. This is a normal process takes place gradually and unnoticed. Skin cells are being updated every 3-4 weeks.
In people with psoriasis this process takes only about 3-7 days. The result is not yet fully formed cells rapidly accumulate on the skin surface, causing the appearance of red, flaky and scaly lesions covered with silvery white scales. It is believed that patients with psoriasis the skin cells are moving faster, because of a weakened immune system.
The immune system is to protect the body, which helps him to fight infection. One of the most important types of cells, which uses the immune system, called T-lymphocytes.
T-cells normally travel around the body, find the infection and to fight with them. In people with psoriasis, they mistakenly attack healthy skin cells. This causes the immune system to produce more T-cells and reproduce new skin cells faster than normal.
It is not clear what exactly causes the disorder of the immune system, although it may be that a certain role is played by certain genes and environmental factors.
Psoriasis is a hereditary. One of three patients with psoriasis has a close relative with the disease. However, it is still unclear what role genetics cause psoriasis. The results of the study show that the development of psoriasis can respond to numerous genes. Likely to make a person more prone to this disease, they can different combination. However, inherited not psoriasis, but only a tendency, that is, the presence of these genes does not mean that you will necessarily develop the disease.
Triggers psoriasis
Many people psoriasis symptoms appear or worsen after a specific event, called a trigger. If you know your triggers, it can help you avoid worsening symptoms. Examples of common triggers:
- damage to the skin, for example. cut, scratch, insect bite or sunburn (so-called. the phenomenon of kebne your);
- alcohol abuse;
- Smoking;
- stress;
- hormonal changes, especially in women (for example, during puberty and menopause);
- some medications, such as lithium, some antimalarial medicines, anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, ACE inhibitors (for the treatment ) and beta blockers (for the treatment of congestive heart failure);
- throat infection — some people, especially children and young adults after streptococcal throat infection is to develop a form of psoriasis called guttate psoriasis although in most cases, when a streptococcal throat infection, psoriasis;
- other disorders of the immune system, such as HIV, which causes the emergence or exacerbation of psoriasis.
Psoriasis is not contagious and therefore cannot spread from one person to another.
The diagnosis of psoriasis
As a rule, the diagnosis of psoriasis sufficient external inspection of the skin.
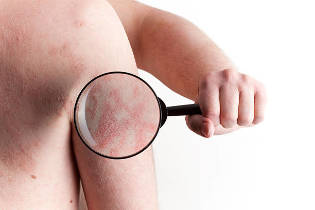
In more rare cases required a biopsy (small sample of skin), which is then sent to a laboratory for examination under a microscope. This allows you to specify a particular type of psoriasis and rule out other skin diseases, like seborrheic dermatitis, lichen planus, simple chronic zoster and pityriasis rosea.
Usually diagnosis and psoriasis treatment is performed under the supervision of a dermatologist — specialist in skin diseases. If your doctor suspects you have psoriatic arthritis, which sometimes occurs as a complication of psoriasis, you may be referred to a rheumatologist. A rheumatologist is a doctor who specializiruetsya is arthritis.
You can take blood tests to rule out other diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and took x-rays of the joints affected by the disease.
Treatment of psoriasis
Completely cure psoriasis is not possible, however, for the treatment, could reduce the severity and frequency of exacerbations. Usually psoriasis treatment is under the supervision of a dermatologist, if participation in the process of the joints is configured to include a rheumatologist. If the symptoms of psoriasis is significantly pronounced and poorly responsive to treatment, your doctor may refer you for admission to the hospital, the Department of dermatology.
A certain method of treatment is applied depending on the type and severity of psoriasis and the skin areas affected. If psoriasis symptoms are mild and not growing, the doctor may be limited to the appointment of the external instruments, for example, in the form of cream. In the acute stage is usually prescribed for more serious treatment of medication inside.
There is a wide range of products, psoriasis treatment, but it can be difficult to determine which is the most effective way. Talk to your doctor if you feel that the treatment is not helping or you have side effects that cause discomfort.
Treatment methods are divided into 3 groups:
- local treatment to the skin to apply creams and lotions;
- phototherapy — the skin is irradiated for a certain type of uv rays;
- system — the ingestion or injection of drugs, which have therapeutic effect on the whole body.
Several different methods of treatment are combined. Patients with psoriasis requires long-term treatment, it is prudent to have a written plan for the medicines manipulation that must be done on a daily basis. Your doctor should be your status regularly and, if necessary, adjust the treatment plan.
























